3. Innovation activity related to products and processes in 2012 to 2014
Innovation activity related to products and processes includes the introduction of product innovations to the market and the implementation of process innovations, as well as any measures that aim at developing and implementing a product or process innovation. Forty-eight per cent of enterprises reported that they had had innovation activity related to products and processes in 2012 to 2014. A majority of them also reported they had introduced product innovations to the market and/or implemented process innovations. Fewer enterprises only reported activities aiming at product and process innovations.
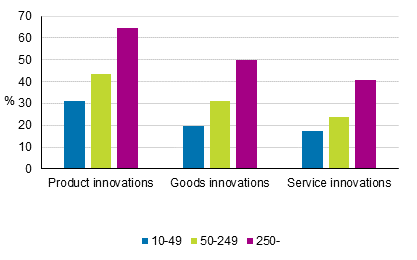
Product innovations introduced to the markets Of the surveyed enterprises, 35 per cent reported that they had introduced product innovations to the markets in 2012 to 2014. In the previous surveys, the proportions were 31 and 33 per cent. Among the smaller enterprises in the survey, i.e. enterprises employing 10 to 49 persons, close on one-third reported new or improved products, 43 per cent of enterprises employing 50 to 249 persons reported innovative products, and among the biggest enterprises, i.e. Those employing at least 250 persons, around two-thirds introduced innovations to the markets.Figure 6. Introduction of product innovations by size category of enterprise in 2012 to 2014, share of enterprises
Enterprises having brought product innovations to the market accounted for 38 per cent in manufacturing and slightly fewer in service enterprises, 32 per cent. In manufacturing, innovations focused on product innovations, whose implementation 35 per cent of manufacturing enterprises reported. In service industries, 14 per cent of enterprises reported product innovations. However, in service industries, service innovations become emphasised as one in four or enterprises in these industries reported they had introduced service innovations to the markets. The share in manufacturing was 14 per cent.
Product innovations were most commonly reported in the manufacture of computer, electronic and optical products, the manufacture of chemicals and chemical products, and in the software industry.Figure 7. Introduction of product innovations by industry in manufacturing in 2012 to 2014, share of enterprises
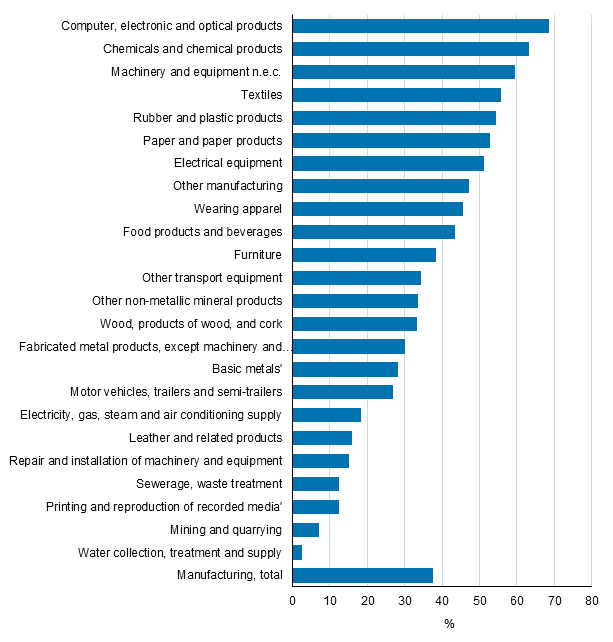
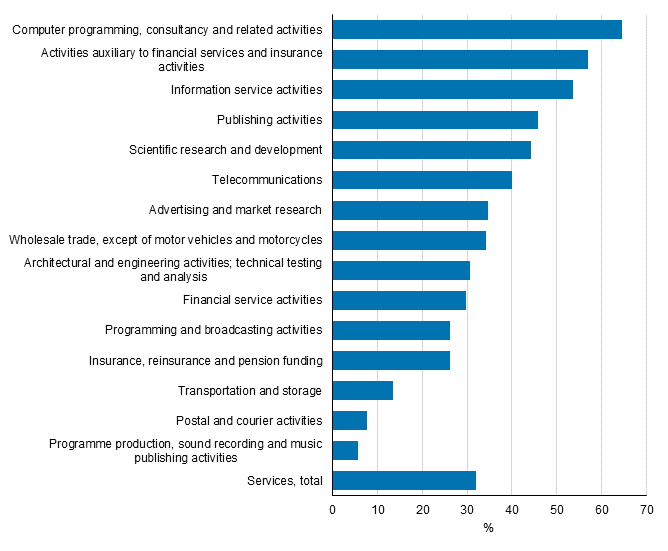
Figure 8. Introduction of product innovations by industry in services in 2012 to 2014, share of enterprises
The developer of an innovation is often times the enterprise that introduced the innovation to the markets, at least partially. Of the enterprises that introduced product innovations to the markets, 79 per cent had developed products themselves and 47 per cent together with other enterprises or organisations. Around one in four, or 27 per cent, had remodelled products developed by others and in 15 per cent of innovations, the developer of the innovation was another enterprise or organisation. There can be several developer profiles and methods within one enterprise.
The developer of innovative services is also often the enterprise that introduced the innovation to the markets. Altogether, 77 per cent of those who introduced service innovations to the markets had developed the innovative services themselves, around one-half had developed innovations together with other enterprises or organisations. Good one-quarter had remodelled services developed by others and more than one in ten introduced an innovation to the markets that had been developed by some other enterprise. Thus, the “profile” of service development is in general terms similar to product development.
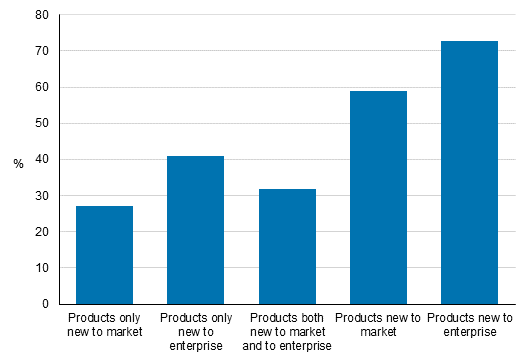
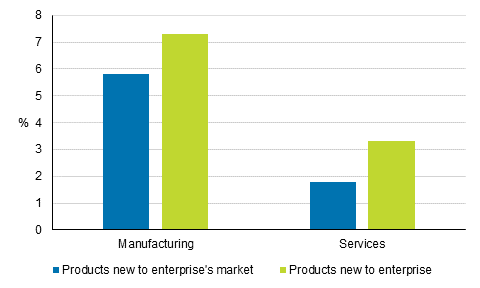
One-fifth of all surveyed enterprises – 59 per cent of enterprises having introduced product innovations to the markets – launched innovations that were new in terms of the enterprise's markets. Altogether, 73 per cent of enterprises having introduced product innovations to the markets – one in four of the surveyed enterprises – in turn, launched innovations that were new from the enterprise's viewpoint but where similar competitive products already existed on the enterprise's markets.Figure 9. Novelty of product innovations in 2012 to 2014, share of enterprises with product innovations
Of the combined turnover of all surveyed enterprises and size categories in 2014, around nine per cent were accumulated from product innovations launched on the markets in 2012 to 2014. This represented 15 per cent of the total turnover of enterprises that launched innovations. In manufacturing, the corresponding proportions were 13 and 17 per cent and in services five and 11 per cent, so in manufacturing, the role of innovations as accumulators of turnover was still larger than in service industries.
The share of turnover from products launched by enterprises that were only new for the enterprise in question was around five per cent of the total turnover of the surveyed enterprises and nine per cent of the combined turnover of enterprises that introduced product innovations to the markets. The share of the 2014 turnover from new products introduced to the markets by enterprises that were also new for the markets was four per cent of the combined turnover of all enterprises and six per cent of the turnover of enterprises that introduced product innovations to the markets. A few years earlier, manufacturing enterprises reported somewhat larger turnover shares from innovative products.Figure 10. Importance of product innovations in enterprises turnover in 2014, share of total turnover of all enterprises
Implementation of process innovations Altogether, 32 per cent of the surveyed enterprises implemented process innovations in 2012 to 2014. In manufacturing, 36 per cent of enterprises reported process innovations and in service industries the share was 29 per cent. Most commonly, enterprises in the manufacture of textiles, manufacture of paper and paper products, manufacture of chemicals and chemical products, operations serving financing and insurance, and in the software industry, as well as in the manufacture of machinery and equipment reported implementation of innovations.
Figure 11. Implementation of process innovations by industry in manufacturing in 2012 to 2014, share of enterprises
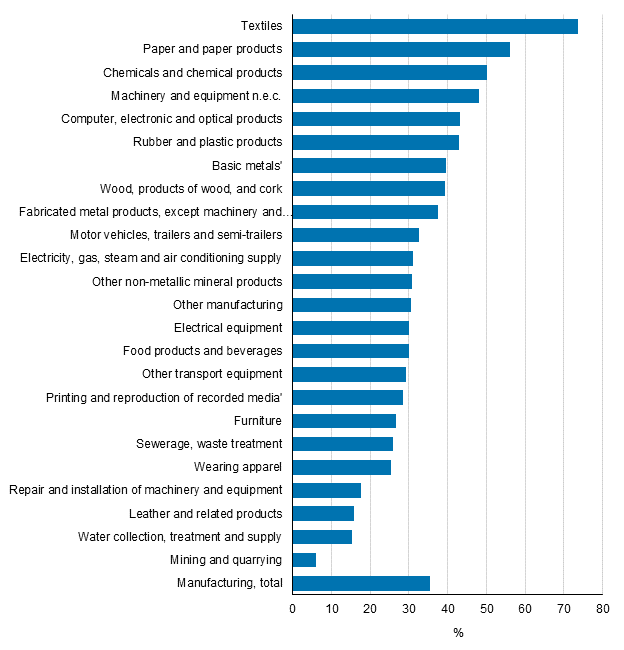
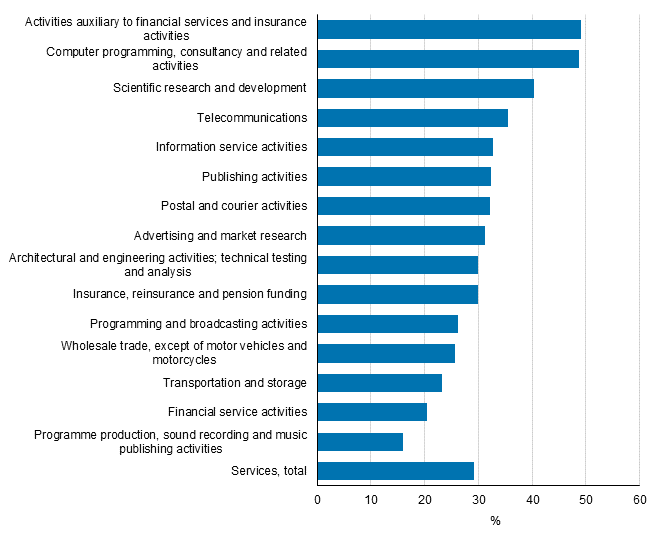
Figure 12. Implementation of process innovations by industry in services in 2012 to 2014, share of enterprises
Process innovations were directed most commonly at the manufacture and production of products, as well as process support functions just as in previous years. One in five enterprises reported implementation of process innovations related to manufacturing, in manufacturing, good one-quarter of enterprises and in service industries, 15 per cent or enterprises. Twenty-one per cent of enterprises reported support functions related innovations, the share being equal in manufacturing and service industries. Eleven per cent of all enterprises had implemented innovations related to logistic solutions or delivery or distribution methods.
Figure 13. Implementation of process innovations by size category of enterprise in 2012 to 2014, share of enterprises
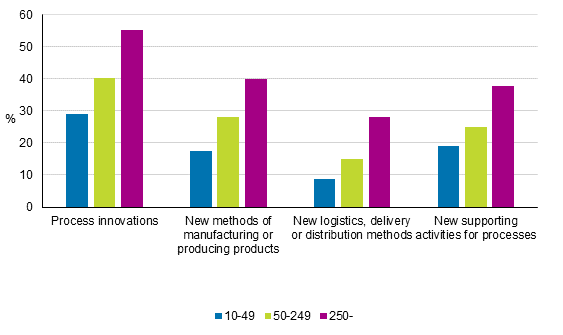
Altogether, 61 per cent of those that had taken process innovations into use had developed the innovations themselves. Around one-half, or 52 per cent, had developed processes together with other enterprises or organisations, and around one in four had adapted or remodelled processes originally developed by others. All in all, 16 per cent of enterprises that implemented process innovations had innovated by taking into use processes developed by other enterprises or organisations.
Projects and activities aiming at product and process innovationsThirty per cent of enterprises reported projects and activities aiming at product and process innovations that had not yet resulted in innovations during the survey period of 2012 to 2014. The projects has either been discontinued or they were still ongoing at the end of 2014.
In manufacturing, 15 per cent and in services, nine per cent of enterprises reported of innovation projects that had been discontinued before completion in 2012 to 2014. Thirty-two per cent of manufacturing enterprises and 23 per cent of service enterprises reported activities aiming at innovations that were still ongoing at the end of 2014.
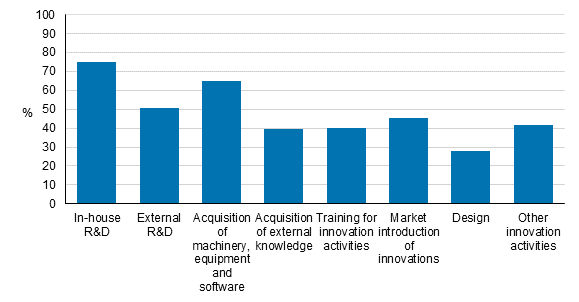
Innovation activities, expenditure and public financial support related to innovation activityLike in the previous survey, three out of four enterprises that had innovated products and processes had their own research and development (R&D) activities in 2012 to 2014. Nearly one-half of these, 47 per cent, had regular R&D activities. Among the smallest surveyed enterprises, 71 per cent of innovators had R&D activities, and among medium-sized enterprises, 84 per cent. Among enterprises employing at least 250 persons and that had developed products or processes, only five per cent reported that they had not had R&D activities in 2012 to 2014.
One-half of enterprises that had developed or implemented product or process innovations had ordered research and development activities from outside the enterprise. In manufacturing, 56 per cent of innovators reported ordered R&D activities and in services, 46 per cent of innovators.
Manufacturing enterprises reported more innovation-related machine and equipment acquisitions (including software and buildings) than service enterprises. In manufacturing, 74 per cent of innovating enterprises had made innovation-related machine and equipment acquisitions, while the corresponding share for service enterprises was 57 per cent. Most commonly, acquisitions were reported by the biggest innovating enterprises in the survey, 78 per cent, while in enterprises employing 10 to 49 persons, 63 per cent reported machine and equipment acquisitions and 69 per cent of medium-sized enterprises.
Around 40 per cent of enterprises involved in innovation activity related to products and processes had acquired existing information from outside of the enterprise to develop innovations. Information acquisition can include acquisition of work protected by copyrights or patented and unpatented inventions. Forty per cent of enterprises with innovation activity had also arranged or acquired personnel training in order to develop and implement product and process innovations. Altogether, 46 per cent of enterprises with innovation activity reported activities related to introducing innovations to the markets. .
Thirty-two per cent of manufacturing enterprises with innovation activity had had design-related activities – either within the enterprise or acquired from elsewhere – within their innovation activities. Correspondingly, 24 per cent of service industry enterprises reported design-related activities. Among the biggest enterprises with innovation activity, good one-half or 55 per cent responded that design had been part of their innovation activity, while among smaller and medium-sized enterprises the corresponding shares were 25 and 29 per cent.
Other innovation activity not included in the above mentioned activities were reported by 42 per cent of enterprises that had developed or implemented products and services.Figure 14. Prevalence of innovation activities in 2012 to 2014, share of enterprises with innovation activity relating to products and processes
Innovation activity expenditure remained in 2014 pretty much on par with the previous couple of years, when the innovation activity expenditure reported by enterprises totalled EUR 6.2 billion. In 2014, innovation activity expenditure was reported to be around EUR six billion. The share of manufacturing was EUR 4.4 billion and that of service industries EUR 1.6 billion.
A majority of innovation activity expenditure was, just like in previous years, directed at R&D activity and in particular at enterprises’ own R&D.Figure 15. Distribution of innovation expenditure in manufacturing in 2014, %
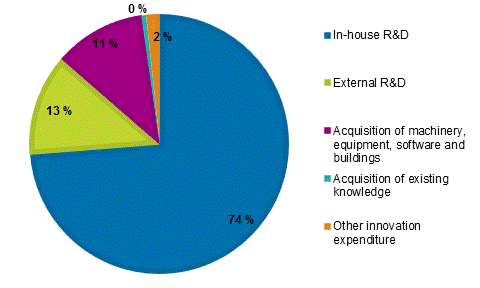
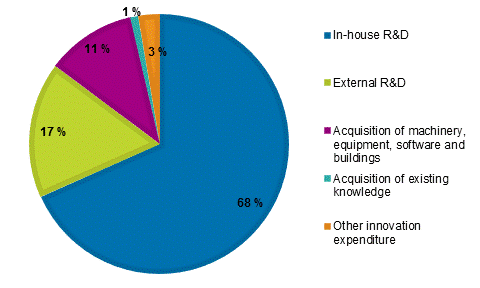
Figure 16. Distribution of innovation expenditure in services in 2014, %
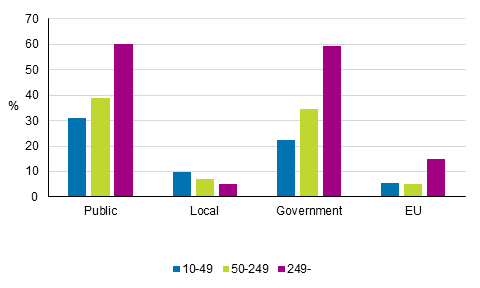
All in all, 35 per cent of enterprises that had developed products or processes received public funding in 2012 to 2014. In manufacturing, 42 per cent had received funding and in service industries, 27 per cent. In the smallest size category, the share of enterprises that had received public funding was 31 per cent, in medium-sized enterprises, 39 per cent and in the largest surveyed enterprises, 60 per cent.
The share of enterprises that had received funding from central government was 27 per cent and the share of enterprises that had received funding from local otr regional authorities was nine per cent among the enterprises with innovation activity. The share of those who had received funding from the EU was six per cent of whom 36 per cent reported they had participated in the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme for Research and Technological Development or the Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation programme.Figure 17. Public funding for innovation activity in 2012 to 2014, share of those involved in product and process related innovation activity
Cooperation related to the development of products and processes
Of enterprises with innovation activity related to products and processes, 38 per cent reported innovation activity-related cooperation. In manufacturing, the share was 41 per cent and in services, 36 per cent. Among the smallest enterprises in the survey, 32 per cent reported cooperation, 47 per cent among medium-sized enterprises and 75 per cent among the largest enterprises with innovation activity.
For enterprises and in case of group enterprises, in addition to intra-group cooperation, the main cooperation partners are found among equipment and material suppliers and customers in the private sector just like in previous surveys. For example, competitors and universities were now mentioned as cooperation partners less frequently than before.Figure 18. External cooperation activity of the enterprise/group related to innovation activity by importance in 2012 to 2014, share of those involved in innovation activity related to products and processes
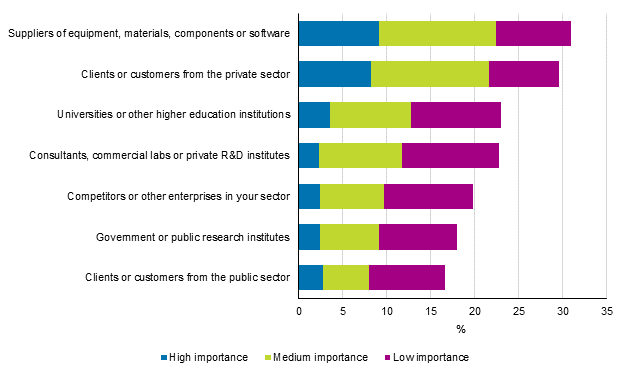
Almost all of the enterprises that had done innovation cooperation had domestic partners. Around two out of three of the enterprises that had done cooperation had partners located in Europe and one in four had partners in the United States. Altogether, 13 per cent reported cooperation in China or India, and 14 per cent reported cooperation partners in other areas.
In practice, when the share of those who had done cooperation is proportioned to all surveyed enterprises, close on one-fifth of the enterprises in the examined industries and size categories have domestic innovation-related cooperation by examined period and, for example, more than one in ten would, according to this, be involved in innovation-related cooperation with partners located in Europe.
Source: Innovation 2014, Statistics Finland
Inquiries: Mervi Niemi 029 551 3263, Heidi Pirkola 029 551 3246, tiede.teknologia@stat.fi
Director in charge: Mari Yl�-Jarkko
Updated 2.6.2016
Official Statistics of Finland (OSF):
Innovation [e-publication].
ISSN=1797-4399. 2014,
3. Innovation activity related to products and processes in 2012 to 2014
. Helsinki: Statistics Finland [referred: 19.4.2025].
Access method: http://stat.fi/til/inn/2014/inn_2014_2016-06-02_kat_003_en.html

