Published: 28 April 2016
Consumption of hard coal grew by 4 per cent in January to March
According to Statistics Finland's preliminary data, the consumption of hard coal increased by four per cent in January to March 2016 compared with the corresponding period of last year. The consumption of hard coal as a fuel in the generation of electricity and heat amounted to 1.1 million tonnes, corresponding to 25 petajoules in energy content. Compared to the average for January to March in the early 2000s, consumption of hard coal was now 32 per cent lower.
Consumption of hard coal, 1,000 tonnes
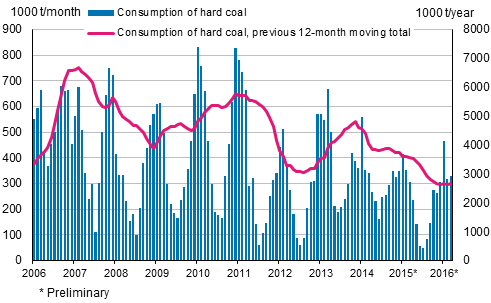
The data for years 2015 and 2016 are preliminary.
In January, the consumption of hard coal grew by 12 per cent from one year previously. The reason for this was the particularly cold weather, which, according to the Finnish Energy Industries, raised the demand for district heating all-time record high. In February, the weather got milder and ten per cent less coal was consumed than one year before. March, in turn, was colder than last year and the consumption of hard coal increased by eight per cent.
Most of the hard coal consumed in Finland is used in combined heat and power production. The use of hard coal in separate production of electricity has clearly diminished in recent years. Condensing power plants have been removed from use and the profitability of the plants in use has weakened due to the fallen price of electricity on the Nordic electricity market.
Hard coal consumption in Finland typically fluctuates seasonally. Some of the fluctuation is explained by the natural variation in the need for electricity and heat between the summer and winter seasons. The difference between statistical reference years is explained by variations in the demand for heating energy and the Nordic water situation, which particularly influences the electricity exchange price and thus the demand for separate production of electricity as well. Therefore, long-term consumption development cannot be deducted from the change in hard coal consumption in successive years.
At the end of March 2016, stocks of hard coal totalled 2.9 million tonnes, or 18 per cent lower than one year earlier.
Source: Consumption of hard coal, Statistics Finland
Inquiries: Ville Maljanen 029 551 2691, energia@stat.fi
Director in charge: Ville Vertanen
Publication in pdf-format (210.1 kB)
- Tables
-
Tables in databases
Pick the data you need into tables, view the data as graphs, or download the data for your use.
Appendix tables
- Appendix table 1. Consumption of hard coal (28.4.2016)
- Appendix table 2: Hard coal stocks, month-end (28.4.2016)
- Revisions in these statistics
-
- Revisions in these statistics (28.4.2016)
Updated 28.04.2016
Official Statistics of Finland (OSF):
Consumption of hard coal [e-publication].
ISSN=1798-2588. March 2016. Helsinki: Statistics Finland [referred: 19.4.2025].
Access method: http://stat.fi/til/kivih/2016/03/kivih_2016_03_2016-04-28_tie_001_en.html

