Published: 12 February 2020
Number of comprehensive schools fell further, educational institutions bigger than before
Corrected on 21 August 2020 . The corrections are indicated in red.
Corrected 8 May 2020: Tables were corrected. The corrections are indicated in red.
According to Statistics Finland’s register of providers of education and register of educational institutions, there were 704 active providers of education and 3,177 educational institutions in which around 1.85 million students pursued studies at the end of 2019. A total of 2,189 comprehensive schools were in operation, 22 per cent of which were joint schools comprising grades 1 to 9. The share of joint schools in comprehensive schools has risen by 10 percentage points in ten years.
Number of comprehensive schools by grade 2010–2019
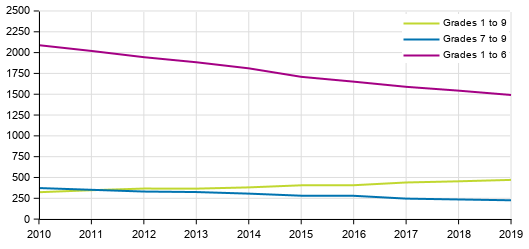
In 2019, there were 2,189 active comprehensive schools and they had a total of 545,300 pupils. The active special education schools at the comprehensive school level numbered 63 and they had 3,600 pupils. Comprehensive schools were more often than earlier joint schools comprising grades 1 to 9. In 2010, the number of active joint schools was 323, while the corresponding figure in 2019 was 471 . In ten years, the share of joint schools in comprehensive schools has risen by 10 percentage points. During the same period, the share of primary schools has decreased by seven percentage points and the share of secondary schools by three percentage points.
Numbers of closed down and merged comprehensive schools and special education schools at the comprehensive school level in 2019
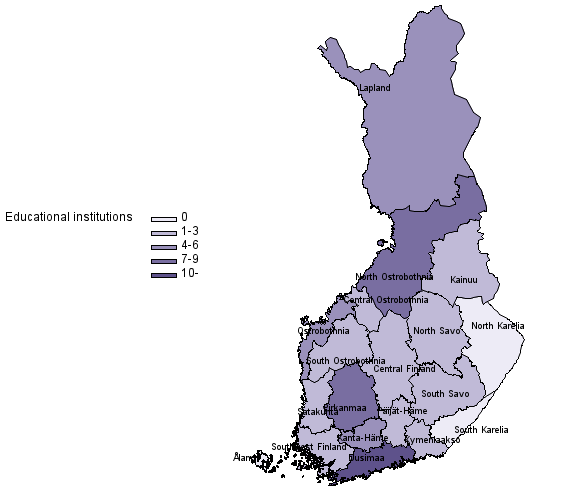
A total of 59 comprehensive schools or comprehensive school level special education schools were closed down or merged with another educational institution. Twelve per cent of them were educational institutions with under 20 pupils, 41 per cent had between 20 and 49 pupils while 47 per cent had at least 50 pupils. Most comprehensive schools and comprehensive school level special education schools were closed down in Uusimaa, 13 in total. Second most were closed down or merged in Pirkanmaa and North Ostrobothnia, seven in both.
Average comprehensive schools size by grade 2010 to 2019
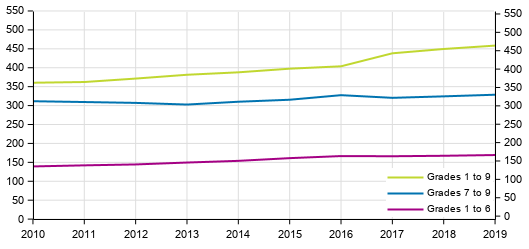
Average number of students (median)
Measured by the average number of students, comprehensive schools are bigger units than before. In ten years, the average size of joint schools has grown most. In 2010, an average of 360 pupils studied at joint schools, while the corresponding figure in 2019 was 464 , i.e. a growth of 29 per cent in the average number of pupils. The growth in the average number of pupils in primary and secondary schools has been lower than in joint schools. In 2010, an average of 139 pupils attended primary schools, while the corresponding figure in 2019 was 169, i.e. a growth of 22 per cent in the average size. The corresponding figures for secondary schools were 312 pupils in 2010 and 329 pupils in 2019, i.e. a growth of six per cent in the average size.
Educational institutions of the school system and numbers of students by type of educational institution in 2019 (The table was corrected on 8 May 2020 and on 21 August 2020)
| Type of educational institution | Number | Change from previous year 1) | Students 2) |
| 11 Comprehensive schools | 2 189 | -47 | 545 300 |
| 12 Comprehensive school level special education schools | 63 | -7 | 3 600 |
| 15 Upper secondary general schools | 335 | -1 | 111 300 |
| 19 Comprehensive and upper secondary general level schools | 42 | 1 | 28 600 |
| 21 Vocational institutes | 84 | 0 | 194 500 |
| 22 Special needs vocational institutes | 5 | - | 5 500 |
| 23 Specialised vocational institutes | 19 | -2 | 12 600 |
| 24 Vocational adult education centres | 10 | -4 | 13 500 |
| 28 Fire, police and security service institutes | 1 | - | 300 |
| 29 Military vocational institutes | 6 | - | .. |
| 41 Universities of applied sciences | 25 | - | 146 100 |
| 42 Universities | 13 | -1 | 159 200 |
| 43 Military academies | 1 | - | 900 |
| 61 Music schools and colleges | 84 | - | 60 900 |
| 62 Sports institutes | 13 | - | 19 200 |
| 63 Folk high schools | 73 | 1 | 15 900 |
| 64 Adult education centres | 177 | -1 | 471 900 |
| 65 Study circle centres | 12 | - | 31 700 |
| 66 Summer universities | 19 | - | 26 000 |
| 99 Other educational institutions | 6 | - | 1 000 |
| Total | 3 177 | -61 | 1 848 000 |
2) The data on the number of students are mainly as on 20 September 2019 and include the number of all students in educational institutions belonging to the type of educational institution independent of the level of education. Data on the number of students at universities, universities of applied sciences, vocational institutions and upper secondary institutions is preliminary.
In 2019, the number of providers of education was in total 11 lower than one year earlier. Of the providers of education, 48 per cent were municipalities or joint municipal authorities, five per cent were central government units and 45 per cent private. The remaining two per cent of the providers of education operated in the region of ┼land. In 2019, five new providers of education were added to the register of providers of education. The number of educational institutions was 63 lower than in the year before.
According to preliminary data for 2019, there were 1.3 million students in education leading to a qualification or degree. These data derive from education statistics compiled by Statistics Finland. Data on the subject are published on Statistics Finland’s websites on the statistics on students and qualifications of educational institutions, pre-primary and comprehensive school education, upper secondary general education, vocational education, university of applied sciences education, university education and adult education of educational institutions.
Contents
- Appendixes:
Source: Education Statistics. Statistics Finland
Inquiries: Mika Witting 029 551 3571, koulutustilastot@stat.fi
Director in charge: Jari Tarkoma
Updated 12.2.2020
Official Statistics of Finland (OSF):
Providers of education and educational institutions [e-publication].
ISSN=1799-5825. 2019. Helsinki: Statistics Finland [referred: 19.4.2025].
Access method: http://stat.fi/til/kjarj/2019/kjarj_2019_2020-02-12_tie_001_en.html

