Published: 26 September 2008
Electricity production with renewable energy sources grew by 25 per cent in 2007
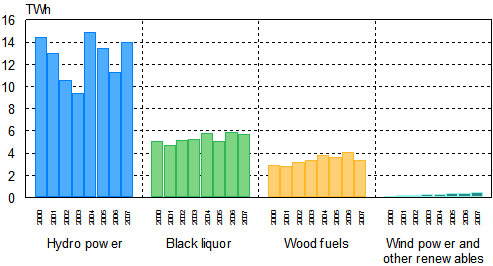
Electricity production with renewable energy sources grew by 25 per cent in 2007, as production of hydro power, which has been decreasing in the past few years, started to increase. Electricity produced with wood fuels decreased by 16 per cent and that produced with black liquor from the forest industry by 3 per cent. The volume of electricity produced with wind power and other renewable energy sources was some 20 per cent higher than in the year before. These data derive from the statistics on production of electricity and heat compiled by Statistics Finland.
In the 2000s over one-half of the electricity produced with renewable energy sources has been generated with hydro power; in 2007 their proportion stood at 59 per cent. Of the electricity produced with renewable energy sources, black liquor from the forest industry accounted for 24 per cent and other wood fuels for 14 per cent. Wind power and other renewable energy sources generated 2 per cent of the renewable electricity.
Production of electricity with renewable energy sources 2000-2007
In 2007 electricity produced in Finland amounted to 77.8 terawatt hours (TWh) or billion kilowatt hours (kWh). This was one per cent down from the year before. District and industrial heat production stayed on level with the previous year. District heat production amounted to 33.5 TWh and that of industrial heat to 61.7 TWh.
Total consumption of electricity was 90 TWh in 2007. The difference in production and consumption was imported from the Nordic countries, Russia and Estonia. Electricity was also exported from Finland to the Nordic countries and Estonia.
In terms of water, the year 2007 was good for Nordic countries; domestic production of hydro power increased by 24 per cent. Production of wind power grew by 23 per cent from the year before. Production of nuclear power grew by 2 per cent. Electricity produced with Nordic hydro power was amply available for import, so the production of domestic condensate electricity decreased by 18 per cent. The volume of electricity generated with combined heat and power production decreased by 3 per cent.
Combined heat and power production remains the most significant mode of electricity production. It accounted for 34 per cent of the electricity produced. Twenty-nine per cent of electricity was produced with nuclear power.
The past few years have been warmer than average, and in 2007 the need of heating energy remained on level with the year before. The volume of heat consumed by industry was also on level with the year before. The volume of combined heat production decreased in both district and industrial heat production and the volume of separate production of heat increased.
Production of electricity and heat by production mode in 2007
| Electricity | District heat | Industrial heat | Total fuels used1) | ||
| TWh | TWh | TWh | PJ | ||
| Separate production of electricity | |||||
| Hydro power | 14.0 | - | - | - | |
| Wind power | 0.2 | - | - | - | |
| Nuclear power | 22.5 | - | - | - | |
| Condensate power2) | 14.4 | - | - | 137.7 | |
| Total | 51.1 | - | - | 137.7 | |
| Combined heat and power production | 26.8 |
25.4 |
49.4 |
451.6 |
|
| Separate heat production | - | 8.1 | 12.3 | 83.9 | |
| Total | 77.8 | 33.5 | 61.7 | 673.2 | |
1) In calculating total primary energy
used, hydro power and wind power are made commensurate with
fuels according to directly obtained electricity (3.6
PJ/TWh).
Total nuclear energy used is calculated at the efficiency ratio of
33 per cent from
produced nuclear power (10.91 PJ/TWh).
2) Condensate power includes condensing power plants, shares of condensate electricity of combined heat and power production plants, and peak gas turbines and similar separate electricity production plants.
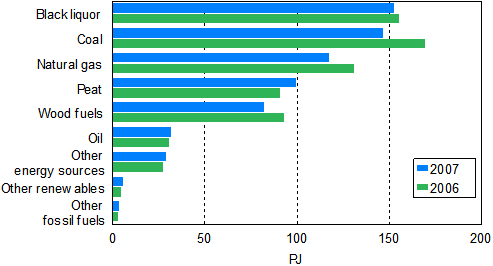
The use of fuels in the production of electricity and heat decreased by 5 per cent in 2007. Use of coal declined most, by 13 per cent. The use of natural gas, wood fuels and black liquor from the forest industry decreased as well. By contrast, use of peat and renewable energy sources (i.a. recycled fuels and biogas) increased.
Use of fuels in electricity and heat production 2006 and 2007
Source: Statistics on production of electricity and heat. Statistics Finland
Inquiries: Ms Minna Niininen +358 9 1734 3549, energia@stat.fi
Acting Director in charge: Mr Matti Parkkinen
Links: Statistics Finland's inquiry on production of electricity and heat
- Reviews
-
- Production of electricity and heat in 2007 (26.9.2008)
- Tables
-
Tables in databases
Pick the data you need into tables, view the data as graphs, or download the data for your use.
Appendix tables
- Figures
-
- Figure 01. Electricity production by production mode 2007 (26.9.2008)
- Figure 02. Electricity production by production mode 2000-2007 (26.9.2008)
- Figure 03. Electricity production by production mode 2000-2007 (26.9.2008)
- Figure 04. Electricity production by energy sources 2000-2007 (26.9.2008)
- Figure 05. Electricity production by energy type 2000-2007 (26.9.2008)
- Figure 06. Electricity produced with renewable energy sources 2000-2007 (26.9.2008)
- Figure 07. Electricity produced with renewable energy sources 2000-2007 (26.9.2008)
- Figure 08. Production of district and industrial heat 2007 (26.9.2008)
- Figure 09. Production of district heat by fuels 2000-2007 (26.9.2008)
- Figure 10. Production of industrial heat by fuels 2000-2007 (26.9.2008)
- Figure 11. Use of fuels by production mode in production of electricity and heat 2007 (26.9.2008)
- Figure 12. Use of fuels in electricity and heat production 2006-2007 (26.9.2008)
- Figure 13. Use of fuels in separate production of electricity 2006-2007 (26.9.2008)
- Figure 14. Use of fuels in combined heat and power production 2006-2007 (26.9.2008)
- Figure 15. Use of fuels in separate production of heat 2006-2007 (26.9.2008)
Last updated 26.9.2008
Official Statistics of Finland (OSF):
Production of electricity and heat [e-publication].
ISSN=1798-5099. 2007. Helsinki: Statistics Finland [referred: 20.4.2025].
Access method: http://stat.fi/til/salatuo/2007/salatuo_2007_2008-09-26_tie_001_en.html

