This set of statistics has been discontinued.
New data are no longer produced from the statistics.
Published: 24 March 2009
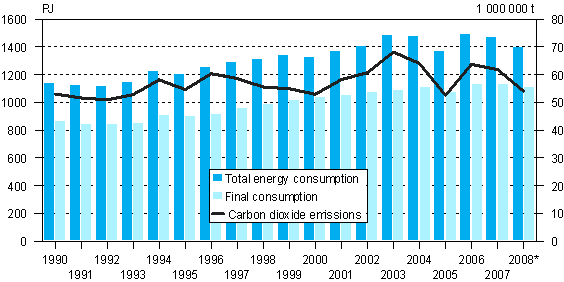
Total energy consumption fell by nearly 5 per cent in 2008
According to Statistics Finland's preliminary data, total energy consumption was 1,400 petajoule (PJ) in 2008, which was 4.7 per cent less than in 2007. Consumption of electricity totalled 87 terawatt hours (TWh), i.e. 3.8 per cent less than in the year before. Carbon dioxide emissions from the production and use of energy diminished by 12,5 per cent compared to the emissions of the previous year.
Total energy consumption decreased from the year before on account of the contraction of industrial output and warm weather. The replacement of coal condensate power with hydro power in the production of electricity also reduced the total consumption of primary energy significantly. Of individual sources of energy, the consumption of coal decreased by 26 per cent (coal includes here hard coal, coke and blast furnace gas). The use of peat in energy production also decreased significantly, over 20 per cent. Two consecutive difficult summers in terms of production conditions resulted in a lack of available peat towards the end of the year.
The year 2008 was exceptional in many respects. The growth of industrial output stalled in the summer and turned to a steep decline towards the end of the year. Industrial output fell by more than 15 per cent year-on-year in December. The prices of fuels and electricity, which showed strong growth in the beginning of the year, turned to a decline towards the end of the year. Production of hydro power in Finland was at a record high level, but when looking at volumes, electricity was also imported more than year before.
Total energy consumption, petajoule (1 petajoule = 1,000 terajoule)
The slide of the economy into recession reduced energy consumption
According to Statistics Finland's preliminary data, growth in GDP slowed down to 0.9 per cent in 2008 from the over 4 per cent of the year before. The quarter-on-quarter changes in GDP in the last two quarters of the year were negative, which means that the economy can be said to be in recession. Output fell in all main manufacturing industries in November.
The fall in industrial output was reflected in industrial consumption of electricity which decreased exceptionally much, by more than 7 per cent. The fall was especially marked in electricity consuming forest industry, whose output declined throughout the year.
Production of hydro power at record level
The very favourable water situation which continued throughout 2008 increased the production of hydro power in Finland to 17 TWh. This corresponds to 23 per cent of total electricity production. In Norway and Sweden the water reservoirs fell below their long-term average towards the end of the year, which reduced Finland's electricity imports from other Nordic countries. At the end of 2008 Finland was a net seller in the Nordic electricity market. However, electricity imports from Russia and Estonia increased, which kept the net imports of electricity growing slightly. The net imports corresponded to 15 per cent of total electricity consumption.
Increased production capacity allowed the production of wind power to keep growing by 40 per cent. However, wind power corresponded to only just under 0.4 per cent of total electricity production. Slightly less electricity was produced with nuclear power than in the record year 2007. Taken as a whole the production of electricity decreased more than its consumption, by 4.7 per cent.
Carbon dioxide emissions of energy production and use diminished 12,5 per cent
The use of fossil fuels and peat fell by 10 per cent from the year before. This reduced carbon dioxide emissions significantly. Use of hard coal decreased both in separate production of electricity and in combined heat and power production. The use of peat in energy production decreased significantly as well after the record year 2007. The share of renewable energy sources grew by nearly 5 per cent from the previous year. The share of renewable energy of total energy consumption stood at 27 per cent.
Use of oil products declined by 2 per cent. Of transportation fuels the consumption of motor gasoline fell by 5 per cent and that of diesel increased by 2 per cent. The act setting out the 2 per cent distribution obligation of biofuels, which entered into force in the beginning of 2008, increased the consumption of biofuels considerably, while simultaneously reducing the consumption of fossil transport fuels.The consumption of light fuel oil used in heating declined by one per cent. Consumption of heavy fuel oil was 8 per cent below the level of the year before.
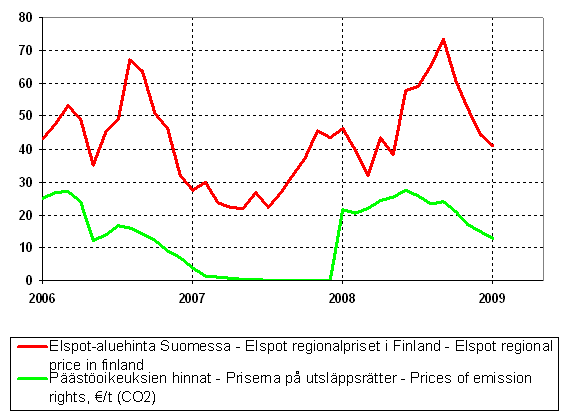
Increase in prices turned to a decline towards the end of the year
The prices of oil products, which had risen strongly in the beginning of the year, turned to a decline in the summer. After reaching record high levels in the summer, in December the prices of liquid fuels were notably below their January levels. The market prices of electricity on the Nordic power exchange Nord Pool and the prices of emission rights also increased strongly in the early part of the year before turning to a decline in the autumn. The prices of hard coal and natural gas, which had been rising nearly the whole year, turned to a decline in the last quarter. The high prices of hard coal, natural gas and peat have been reflected also in the price of district heat, which rose by over 10 per cent from the year before.
Price development of electricity market prices and emission rights 2006-
Preliminary Energy Statistics 2008
Sources: Preliminary energy statistics 2008. Statistics Finland.
Inquiries: Mr Anssi Vuorio +358 9 1734 2685, Ms Kirsi-Marja Aalto (09) 1734 3442, energia@stat.fi
Director in charge: Ms Leena Storgårds
- Tables
-
Appendix tables
- Preliminary Energy Statistics 2008 - Tables (Excel) (24.3.2009)
- Table 01. Total Energy Consumption by Source (Excel) (24.3.2009)
- Table 02. Supplies and Total Consumption of Electricity (Excel) (24.3.2009)
- Table 03. Energy Imports by Country of Origin in 2008 (Excel) (24.3.2009)
- Table 04. Energy Exports by Recipient Country in 2008 (Excel) (24.3.2009)
- Table 05. Consumer Prices of Liquid Fuels (Excel) (24.3.2009)
- Table 06. Consumer Prices of Hard Coal, Natural Gas and Domestic Fuels in Heat Production (Excel) (24.3.2009)
- Table 07. Price of Natural Gas by Type of Consumer (Excel) (24.3.2009)
- Table 08. Price of Electricity by Type of Consumer (Excel) (24.3.2009)
- Table 09. Price of District Heating by Type of Consumer (Excel) (24.3.2009)
- Table 10. Excise Taxes, Value Added Taxes and Fiscal Charges and Fees Included in Consumer Prices of Some Energy Sources (Excel) (24.3.2009)
- Table 11. Energy Taxes, Precautionary Stock Fees and Oil Pollution Fees (Excel) (24.3.2009)
- Figures
-
- Electricity Consumption by Sector 1970-2008 (24.3.2009)
- Electricity Generation Capacity in Peak Load Period (24.3.2009)
- Electricity consumption by sector 2008 (24.3.2009)
- Electricity supply 1970-2008 (24.3.2009)
- Energy and Electricity Intensity 1970-2008 (24.3.2009)
- Figure 01. Changes in GDP, Final energy consumption and electricity consumption 1995-, % (24.3.2009)
- Figure 02. Carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuels and peat use 1990-, Mt (24.3.2009)
- Figure 03. Coal consumption 1993-, mill. t (24.3.2009)
- Figure 04. Consumption of natural gas 1993-, bn m3 (24.3.2009)
- Figure 05. Peat consumption 1993-, TWh (24.3.2009)
- Figure 06. Domestic oil deliveries 1993-, mill. t (24.3.2009)
- Figure 07. Import prices of oil 1997-, /t (24.3.2009)
- Figure 08. Consumer prices of principal oil products 1995-, c/l (24.3.2009)
- Figure 09. Fuel Prices in Heat Production 1995-, /MWh (24.3.2009)
- Figure 10. Fuel prices in electricity production 1995-, /MWh (24.3.2009)
- Figure 11. Price of electricity by type of consumer 1994-, c/kWh (24.3.2009)
- Figure 12. Average monthly spotprices at the Nord Pool power exchange 1998-, /MWh (24.3.2009)
- Final energy consumption by sector 2007-2008 (24.3.2009)
- Final energy consumption by sector 2008 (24.3.2009)
- Finland's Greenhouse Gas Emissions 1990-2008 (24.3.2009)
- Imports and Exports of Electricity 1990-2008 (24.3.2009)
- Production of District Heat 1970-2008 (24.3.2009)
- Renewable energy as a proportion of final energy consumption in 2006, and the target for 2020 (24.3.2009)
- Share of Renewables 2008 (24.3.2009)
- Total Energy Consumption 1970-2008 (24.3.2009)
- Total Energy Consumption 2007-2008 (24.3.2009)
- Total Energy Consumption 2008 (24.3.2009)
- Total Energy Consumption and Final Energy Consumption 1970-2008 (24.3.2009)
- Total energy consumption, final consumption and carbon dioxide emissions (24.3.2009)
Last updated 24.3.2009
Statistics:
Energy supply, consumption and prices [e-publication].
ISSN=1798-338X. 4th quarter 2008. Helsinki: Statistics Finland [referred: 10.3.2025].
Access method: http://stat.fi/til/ehkh/2008/04/ehkh_2008_04_2009-03-24_tie_001_en.html