Published: 21 April 2020
General government deficit 1.1 per cent and debt 59.4 per cent relative to GDP in 2019
According to the revised preliminary data reported by Statistics Finland to Eurostat, general government deficit was 1.1 per cent relative to gross domestic product in 2019. The deficit was clearly below the reference value of the European Union’s Stability and Growth Pact, which is three per cent relative to gross domestic product. General government EDP debt, or consolidated gross debt, was 59.4 per cent at the end of 2019 relative to gross domestic product. The ratio of debt to GDP is below the reference value of 60 per cent.
General government EDP deficit (-) relative to GDP
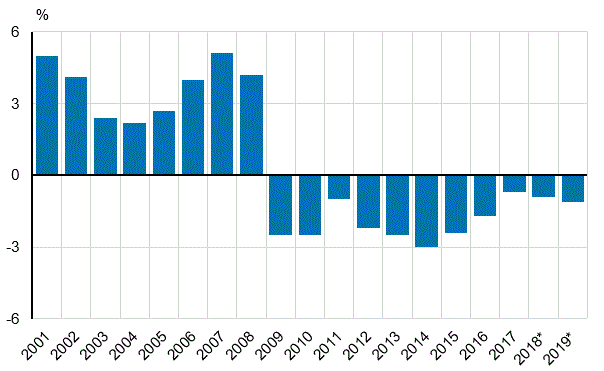
In 2019, general government deficit, or net borrowing according to national accounts, was EUR 2.7 billion. The financial position of general government weakened by around EUR 700 million from the year before. The financial position of local government weakened most, by around EUR 900 million compared to 2018. This was particularly due to significant increases in the sector’s consumption expenditure and investments. In 2019, local government sector deficit, or net borrowing, was EUR 2.9 billion.
From 2018, central government deficit decreased by EUR 110 million, but still remained clearly in deficit. The deficit of central government stood at EUR 2.8 billion in 2019.
Social security funds are divided into employment pension schemes and other social security funds. The employment pension schemes’ surplus was EUR 2.2 billion in 2019, i.e. approximately the same as in the previous year. The surplus of other social security funds was EUR 0.7 billion in 2019.
General government EDP debt relative to GDP
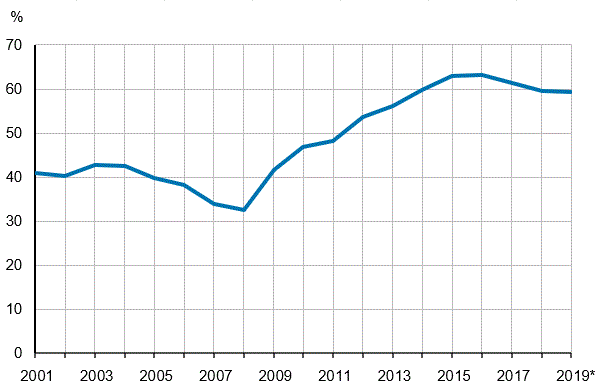
Consolidated general government gross debt (EDP debt) amounted to EUR 142.5 billion at the end of 2019. The debt grew by around EUR three billion in 2019. Central government debt grew by EUR 1.4 billion and local government debt grew by EUR 2.9 billion. The debt of social security funds decreased by EUR 0.9 billion. The increase in consolidated items between general government by EUR 229 million contributed to the debt of the entire general government sector growing by EUR one billion in 2019. The EDP debt describes general government’s debt to the other sectors of the economy and to the rest of the world, and its development is influenced by changes in both the unconsolidated gross debt and the internal general government debt.
In the publication of general government debt by quarter on 16 March, a review was made to the general government debt for the years 2015 to 2018 as the Manual on Government Deficit and Debt (MGDD) was updated. The data for 2019 have been compiled on the same principle. More information on the processing can be found in the decision on rearrangement of transactions in activity under Finnvera’s commitment to compensate credit and guarantee losses in national accounts . These corresponding recordings have now also been entered into the database and appendix tables containing annual data which are published in connection with the statistics on general government deficit and debt.
Eurostat will publish preliminary data on Member States on 21 April 2020.
About the content and concepts of the statistics
General government surplus/deficit refers to net lending/borrowing according to the sector accounts of national accounts, which is the difference between the total revenue and expenditure. For instance, in the case of local government, the concept differs from the surplus/deficit of the accounting period according to the profit and loss accounts of municipalities and joint municipal authorities included in the sector. The key difference concerns investments, which are recorded in national accounts as expenditure as such.
In general government accounts, the European Financial Stability Facility EFSF is, based on Eurostat's decision, handled so that the EFSF's borrowing is recorded as part of the gross government debt of the countries that have provided guarantees. The loan received by the beneficiary country from the EFSF is recorded as if it had been received from the countries in the euro area that have provided guarantees and these countries in turn owe the corresponding amount to the EFSF. As a result, the EDP gross debt of the countries that provided guarantees grows but the net debt remains unchanged because the countries have a similar receivable from the beneficiary country. The gross government debt to be recorded for each country on the loans granted by the EFSF is calculated by dividing the loan granted to the beneficiary country by the contribution key (based on the share in the ECB's capital of each country participating in the support operations).
At the end of 2019, Finland's general government debt includes EUR 3,401 million of debt granted by the EFSF to beneficiary countries. At the end of 2018, the amount was the same. Corresponding treatment does not apply to the European Stability Mechanism (ESM).
Central government's EDP debt differs as a concept from the central government debt published by the State Treasury. Central government's EDP debt includes loans granted to beneficiary countries by the European Financial Stability Facility EFSF, received cash collateral related to derivative contracts, the capital of the Nuclear Waste Management Fund, debts generated from investments in central government's PPP (public-private partnership) projects, and coins that are in circulation. In National Accounts, central government is also a broader concept than the budget and financial economy (http://www.stat.fi/meta/luokitukset/_linkki/julkisyhteisot.html). However, the State Pension Fund is classified as a social security fund. The valuation principle for both debt concepts is the nominal value, where the effect of currency swaps is taken into account. When these differences are taken into consideration, we reach the central government non-consolidated gross debt in accordance with the EDP concept (Appendix table 2). In 2019, the State Treasury's central government debt EUR 106.4 billion + conceptual differences of the debt EUR 7.8 billion + differences caused by the sector delimitation EUR 4.0 billion = central government gross debt EUR 118.2 billion. The valuation principle for both debt concepts is the nominal value, where the effect of interest-rate contracts and currency swaps is taken into account.
A list of units belonging to general government (only in Finnish) can be found at http://www.stat.fi/meta/luokitukset/_linkki/julkisyhteisot.html .
Source: General government deficit and debt. Statistics Finland
Inquiries: Lotta Sjöblom 029 551 3342, Antti Suutari 029 551 3257, financial.accounts@stat.fi
Director in charge: Jan Nokkala
Publication in pdf-format (256.5 kB)
- Tables
-
Tables in databases
Pick the data you need into tables, view the data as graphs, or download the data for your use.
Appendix tables
- Figures
- Revisions in these statistics
-
- Revisions in these statistics (21.4.2020)
Updated 21.4.2020
Official Statistics of Finland (OSF):
General government deficit and debt [e-publication].
ISSN=1799-5914. 2019. Helsinki: Statistics Finland [referred: 20.4.2025].
Access method: http://stat.fi/til/jali/2019/jali_2019_2020-04-21_tie_001_en.html

